
Renewable energy sources are a group of sources that generate electrical power and other useful forms of energy without using fossil fuels or other polluting sources. They include biomass, hydroelectricity, solar, and geothermal energy. These technologies are likely to play a significant role in the global movement for climate change.
Solar and wind energy are the fastest growing sources of electricity in the U.S. and around the world. These technologies are expected to continue growing worldwide. The Appalachian Mountains, Great Plains and Great Plains are home to the greatest concentrations of wind resources. Photovoltaics has the highest growth rate of any type of solar technology. By 2020, there will be 139 GW global capacity. These technologies can also provide electricity.

Since thousands of years, biomass has been used to heat and cook food. It can be derived from plant residues, agricultural waste, and forest by-products. It can also fermented to make hydrogen or biodiesel.
Hydropower has been around for many years. Actually, hydropower is one the oldest sources of electricity. It has historically been a reliable power source. Relying on renewables comes with its own set of challenges.
Grid integration of these technologies becomes difficult due to their intermittent nature. This is especially true when there are high levels of deployment. System costs rise as variable renewables increase in percentage.
While solar and wind can be used in a relatively simple manner, it can prove difficult to integrate them into a grid. This is due to the need for backup power generation. It is also possible for weather conditions or the time of day to affect how much sunlight is available. In addition, technology cost and efficiency can have an impact on how much energy you use.
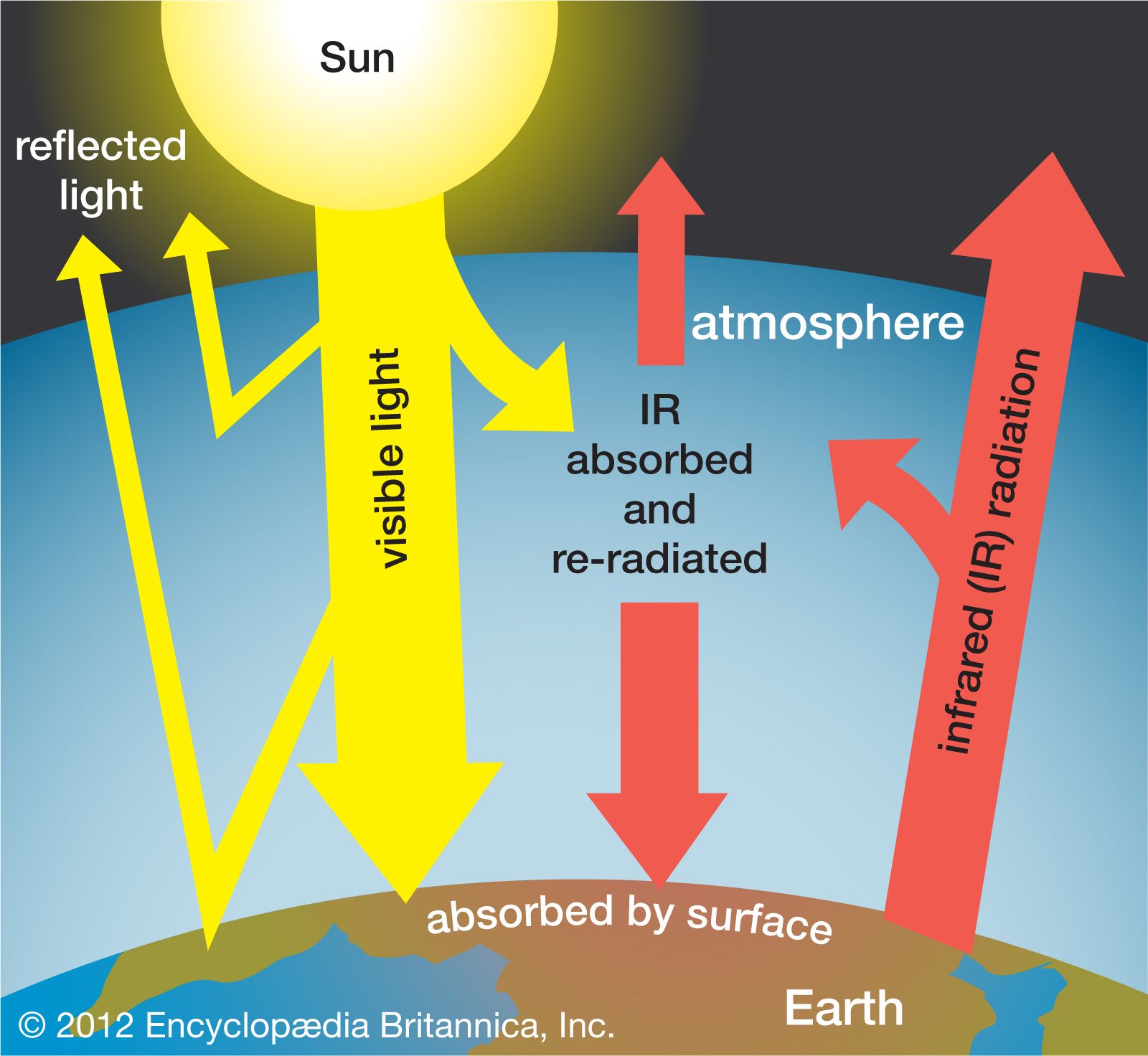
Up to 29 percent of the global electricity generation is expected to come from solar and wind power by 2020. The increased use of these technologies will help to reduce carbon dioxide emissions, reducing the global carbon footprint.
Geothermal energy is a source of heat that dates back to ancient times. This source of heat has been used for space heating since the time of the Romans. Unfortunately, today it is not easily accessible. Enhanced geothermal systems use advanced drilling techniques and fluid injection to access this resource.
The most common form of biomass is wood. You can get it from trees, plant matter, and municipal solid waste. Wood can be transformed into biofuels, like ethanol. It can also be used for direct heating, in the case of domestic hot water units.
A number of countries are utilizing these resources. In fact, China and India have pledged 78 GWe of capacity by 2030, which would lead to a 9% reduction in per capita CO2 emissions. Germany currently hosts some of the world's largest power-to gas plants. These include a 6MW unit at Energiepark Mainz, and a 20MW unit at Element Eins.
FAQ
What is the effect of climate change upon biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change is having a wide range of effects on biodiversity as well as ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changing extreme weather events and sea level, as well as an increase in acidity in oceans, are all issues that affect wildlife and ecosystems.
Changes in climate can lead to shifts within habitat areas, disruptions in food chains, or changes in population numbers, or both. This could have dramatic implications for biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Hydrological changes can also impact water availability for aquatic species.
Climate change also causes rising temperatures, more frequent extremes like droughts and flooding. This puts additional stress on fragile systems like coral reefs and tropical rainforests. It is estimated that up to 30% of animal species could become extinct due to climate change by 2050, which would spark a cascade of further losses within ecological communities.
Climate change is a serious threat to biodiversity as well as human societies that rely on functioning ecosystems for food and fresh water. At all levels, efforts should be made to decrease global warming trends. Future damage should be avoided if possible through careful management.
What is the potential of new technologies to combat climate changes?
This global problem is a huge challenge that new technologies can address. Advances in applied science make it possible to move to a more sustainable future.
New methods for carbon capture or sequestration can be used to lower greenhouse gases. Additionally, improved agricultural practices can reduce the emissions of livestock and soil erosion. Smart grid technology is also possible to be integrated into existing power infrastructure, resulting in an efficiency boost. Furthermore, improved building design can help decrease energy consumption.
The latest synthetic biology methods allow scientists to create organisms that can use green sources of fuel like the CO2 laser as biofuels or alternative feedstocks. This could be a major shift in transportation if there is a shift away from petrol-based vehicles to electric cars powered solely by renewable sources.
Finally, increased investments in digital technology or AI can provide people with more information on their ecological footprints across borders. This will allow them to make more informed decisions regarding their consumption habits. Ultimately, understanding our role in carbon production is paramount allowing us all to be better stewards of our planet.
What is the current climate like? How is it changing?
The current climate is characterized by unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes have already had a significant impact on ecosystems across the globe, leading to habitat loss and extinction. They are also threatening millions of people's lives and livelihoods, particularly in areas where there is already resource scarcity.
Human activity has led to an increase in extreme weather events such as hurricanes, cyclones, floods, wildfires, etc. This trend is expected to continue into the future as temperatures continue to climb.
Climate change has global consequences. It can affect everything, from food insecurity and displacement to communities that are forced to relocate due to severe weather events or rising sea levels. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
While some countries have made progress in reducing carbon emissions, or implementing renewable energy initiatives, global action has not been taken at the level necessary to combat these changes. To prevent further destruction and devastation caused by climate change, all countries must work together to take immediate action and plan for adaptation in an ever-changing world.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to reduce your carbon footprint and fight climate change
There are many steps that you can take to reduce your carbon footprint and help fight climate change. You can start by investing in energy efficient appliances, lighting, insulation, and other energy-saving measures in your home. You can also save energy by unplugging electronics when not in use, using public transit, walking rather than driving, and turning down the temperature on your thermostat in the winter and summer months.
Second, ensure you recycle all materials and compost food scraps. They won't end up in landfills that release methane gas to the atmosphere. Third, you can plant trees around the house to provide shade and natural cooling. Vegetation absorbs carbon dioxide in the air. Finally, consider purchasing products with minimal packaging or sustainable labelings such as organic cotton or FSC-certified wood which means it's been sustainably managed over time to ensure forest health.
In addition to reducing your own personal emissions, you can also support organizations that focus on reducing global emissions such as Emissions Reduction Alberta; Climate Change Solutions; The Pembina Institute or The Nature Conservancy Canada work towards lowering emissions through clean energy investments and international initiatives like ICLEI - Local Governments for Sustainability's urban sustainability strategies program.
Everyday changes can be made to help fight climate change.