
The Sun is a massive ball of hot Plasma and is very close to Earth. Its energy output has fallen over the past five decades. This isn't the sole reason for the recent temperature surge. Over the same period, greenhouse gas levels have skyrocketed. As a result, our climate has been boosted by about 0.8 degrees Celsius.
One explanation for the warming is carbon dioxide resulting from fossil fuel combustion. This gas is integral to photosynthesis in plants and breaks down when it absorbs excess heat. The plants will soon die as there is more of the noxious gas. Only microbial life will be left to take over the planet.

The number sunspots found on the surface of the earth is an indicator of solar activity. There are two eleven-year cycles. The sun was much larger during the first cycle than it is now. However, it will gradually shrink in size over the next few decades. Eventually, it will become a red giant. Its gravity pulls on the planet, and its orbit is affected.
A 22-year magnetic period is also available for the Sun. The solar cycle is not correlated with the average temperature in the lower atmosphere. Is the sun getting hotter? Although we don’t know for certain, we do know that the sun is becoming more intense.
Ocean currents, as well as the formation of mountain ranges, are other factors that influence our planet's temperature. All of these factors are tied to the grand climate cycle. If the cycle was to change in the next few years, then we might see an abrupt shift in temperature.
Another factor is Earth's natural tidal factors. These are the result the moon's relationship with Earth. When the Moon is between the Earth and the sun, tides are lower. Large tidal changes are due to the oceans bulging toward the sun. But, when the Moon moves far from Earth, the tides will be higher. The latter is not the case, fortunately for us humans.
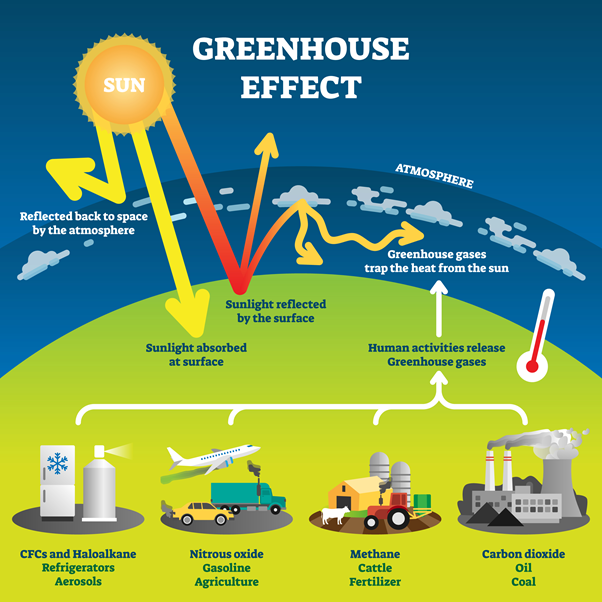
Another important factor that makes our weather system the Sun's most powerful and influential player is the large amount of oxygen it contains. This gas is vital to the existence of life on this planet. However, a decrease in its availability will result in it becoming very difficult to sustain. Plants will eventually become extinct and only microbial life is left. This will make our planet uninhabitable.
Finally, the sun, as a main sequence star is not perfect. Some of its parts are too small, but the sun itself is a massive ball of hot plasma. Its intensity has increased by around 40% since the sun's creation. It is approximately halfway through its lifetime.
Despite its age it still contributes significantly to the climate. Even if the planet doesn't heat up in the next century, its outer atmosphere will continue to have a negative effect on Earth's orbit.
FAQ
What are the causes for climate change
Climate change is a global phenomenon that has been driven by an increase in human-generated greenhouse gases emitted into our atmosphere, primarily due to fossil fuel burning for electricity and transportation. These greenhouse gases trap more heat from the sun, which causes global warming.
Climate change can also be caused by population growth, land clearing, destruction of ecosystems and energy consumption, over-grazing, and deforestation. This further reduces the number of naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. Climate change may also be caused by natural factors such as changes to solar radiation.
These human activities together result in Earth experiencing an overloading of its energy budget. This has caused an average global rise of 1° Celsius over pre-industrial time. Glaciers are melting faster than they become and sea levels are rising as the oceans absorb most of the heat energy. Other adverse consequences include water shortages and droughts as well as extreme weather events, such as flooding and hurricanes, which are often caused by heavy rains on soils.
To protect ourselves from further damage, it is essential for us to reduce our carbon footprint and start curbing our emissions now so that we have a fighting chance against the already significant impacts of climate change. Reducing our dependence on fossil fuels for electricity production is crucial alongside investing in renewable sources - think wind turbines or solar panels - which do not emit any harmful pollutants into the environment. You can also restore some balance in these delicate cycles of the planets that sustain us, such as reforestation.
What are some of the solutions proposed to climate change? How effective are they?
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our times, requiring urgent attention from governments, businesses, and citizens alike. An unstable climate system can be seen in rising temperatures, extreme events, high sea levels, and melting of polar ice. Many solutions have been offered to this problem, ranging from technological and behavioral solutions to geoengineering.
Technological solutions: A wide range of technologies have been used to address climate change. These include renewable energy sources like solar power and wind power that provide reliable sources for clean energy while causing minimal harm to the environment. Electric cars powered with renewable energy could dramatically reduce pollution in cities and replace petrol vehicles. Reforestation projects are another technological option that aim to increase carbon sequestration, soil and trees. They also provide coastal protection systems to protect vulnerable areas from rising ocean levels.
Simple behavioral changes can help reduce emissions and limit future climate disruption. So, for example, buying locally-produced goods reduces the transport costs associated with food transport. Also, using public or active transport instead of personal cars optimizes the use and reduces cost and air pollution. Additionally, home insulation that is more efficient can reduce dependence on gas boilers for heating your homes and lowers emissions.
Geo-engineering (GEO): This involves large-scale interventions into natural systems that may be too risky because of potentially unforeseeable consequences.
The effectiveness of these solutions depends on how committed producers are to investing in green alternatives. At the moment, electric Cars can be more expensive than petrol-powered versions. However, market forces that cannot guarantee their utility over the long term try to increase consumer awareness about their efficiency. This is why mandated alternative solutions via policy measures is one way forward. However regulatory bodies need to be willing to engage further players. While nontechnological solutions may work at one level, solving global warming must be tackled by all parties.
What is the status of international efforts to tackle climate change?
The international effort to tackle climate change has reached a new level of unity and momentum. Countries all over the world are now working together to reduce emissions, improve resilience against impacts, as well as invest in renewable energy sources.
At the global level, the Paris Agreement has galvanized collective action and serves as a framework for individual countries to set voluntary targets for reducing emissions. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change and (UNFCCC) provides political guidance, as well as piloting initiatives such a carbon market.
Progress is also being made in specific regions; for example, The European Green Deal is a comprehensive package of legislation aimed at recreating Europe's economy with sustainability at its core, while countries of the African continent have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative which aims to increase Africa's share of global renewable energy production.
Apart from policy changes, action is visible across sectors and industry. Cities are actively transitioning to sustainable public transport systems. Society at large is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Companies have been innovating technologies to lower emissions. Investors are switching away from fossil fuels to invest in renewables.
The wealthy countries represented under the OECD committee have adopted common standards for reporting national actions on climate change through the Common Reporting Framework (CFR) called the 2021 Guidelines.
All of these efforts show an unprecedented focus on climate action. To meet climate goals, both governments and civil society must continue to build on the momentum.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Make Your Home More Energy-Efficient and Combat Climate Change
You can make your home more efficient and reduce your carbon footprint. It will also save you money on your utility bills.
You must ensure that your home is properly insulated. Check for drafts, ensure doors and windows are properly installed, and then seal any gaps or cracks with caulking.
Insulate your walls, ceilings, and floors to maximize energy efficiency. You should inspect your attic and other areas for leaks.
Lighting accounts for up to 18% of total household electricity usage so make sure you switch to LED light bulbs which use up to 80% less electricity than traditional incandescent ones! Additionally, motion sensors and timers can help you save money by automatically turning off lights when necessary.
Replacing an old boiler or furnace can dramatically reduce energy bills as newer models are much more efficient. A programmable thermostat can be used to set temperature settings based on the time people are at home and away.
Double-glazing windows can be replaced with better insulation. They also prevent heat from escaping through the glass. Low-flow showerheads reduce water consumption and maintain adequate pressure.
ENERGY STAR rated devices use 50 % less energy than non-certified appliances. Don't forget about small details such as unplugging electronic devices like phone chargers or TV boxes when not in use - this could save you a significant amount of energy over time!
Overall, these few steps can significantly lower your impact on climate change, decrease monthly electricity costs, making living at home much more efficient!