The phrase "climate under crisis" has become synonymous to the dangers posed by global warming. The term has also been used to urge aggressive climate change mitigation. The climate crisis does not only concern climate change. It is about how people react to the climate crisis and make decisions. This can have a major psychological impact.
Climate in Crisis examines how climate change and global warming affect people, communities and the planet. This book examines the impacts of climate change on Indigenous communities and the ways they are impacted.
Many environmental activists are speaking up against climate change because it will lead to more extreme weather. Some of these people are scientists and activists. Other people are farmers, who are adopting more sustainable practices.

The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change states that the climate of Earth is changing rapidly. And if we don't act, we could see an increase in extreme heat, heavy precipitation, and drought. Even the world's ocean levels have been rising. This means some changes are irreversible.
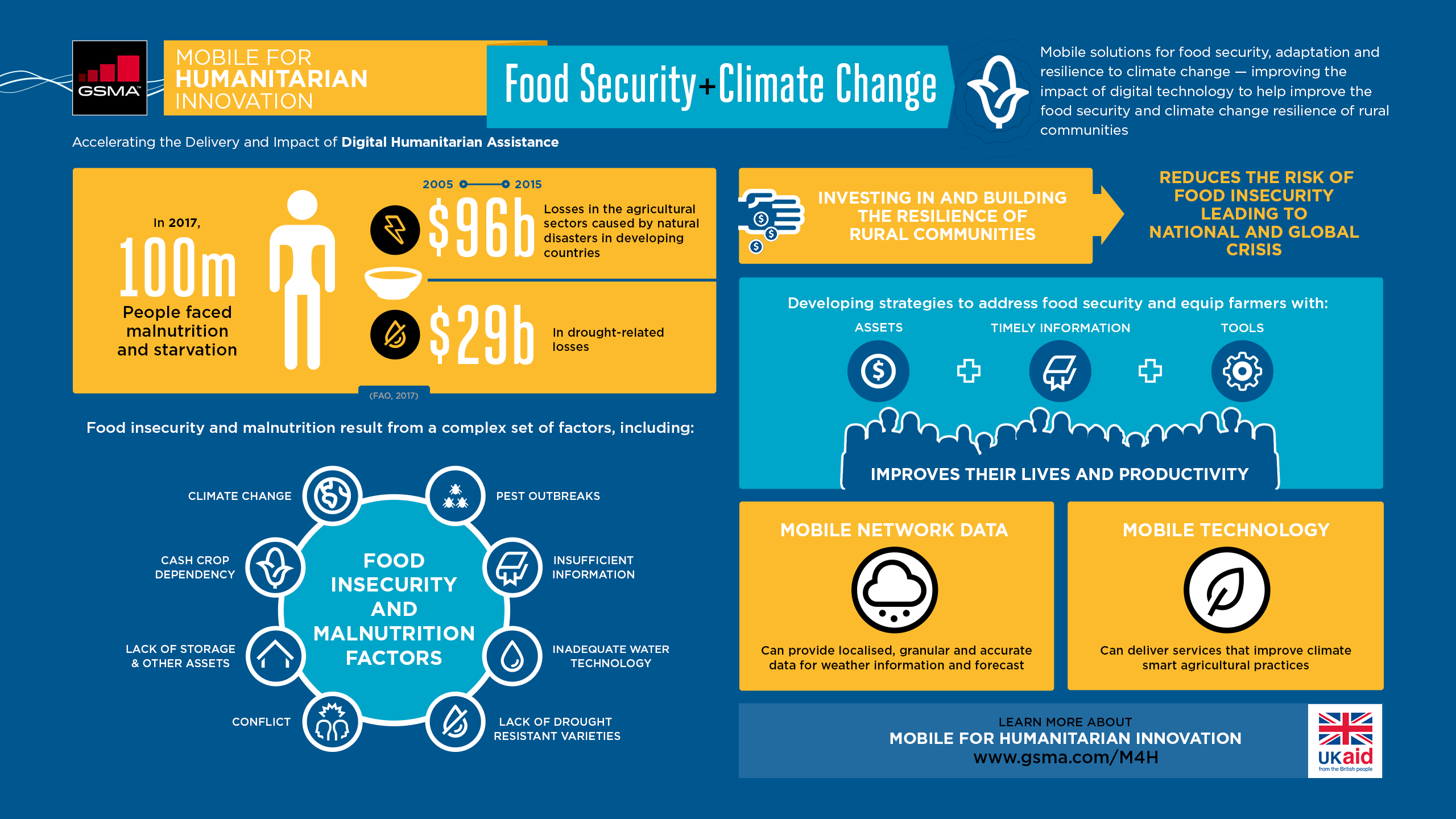
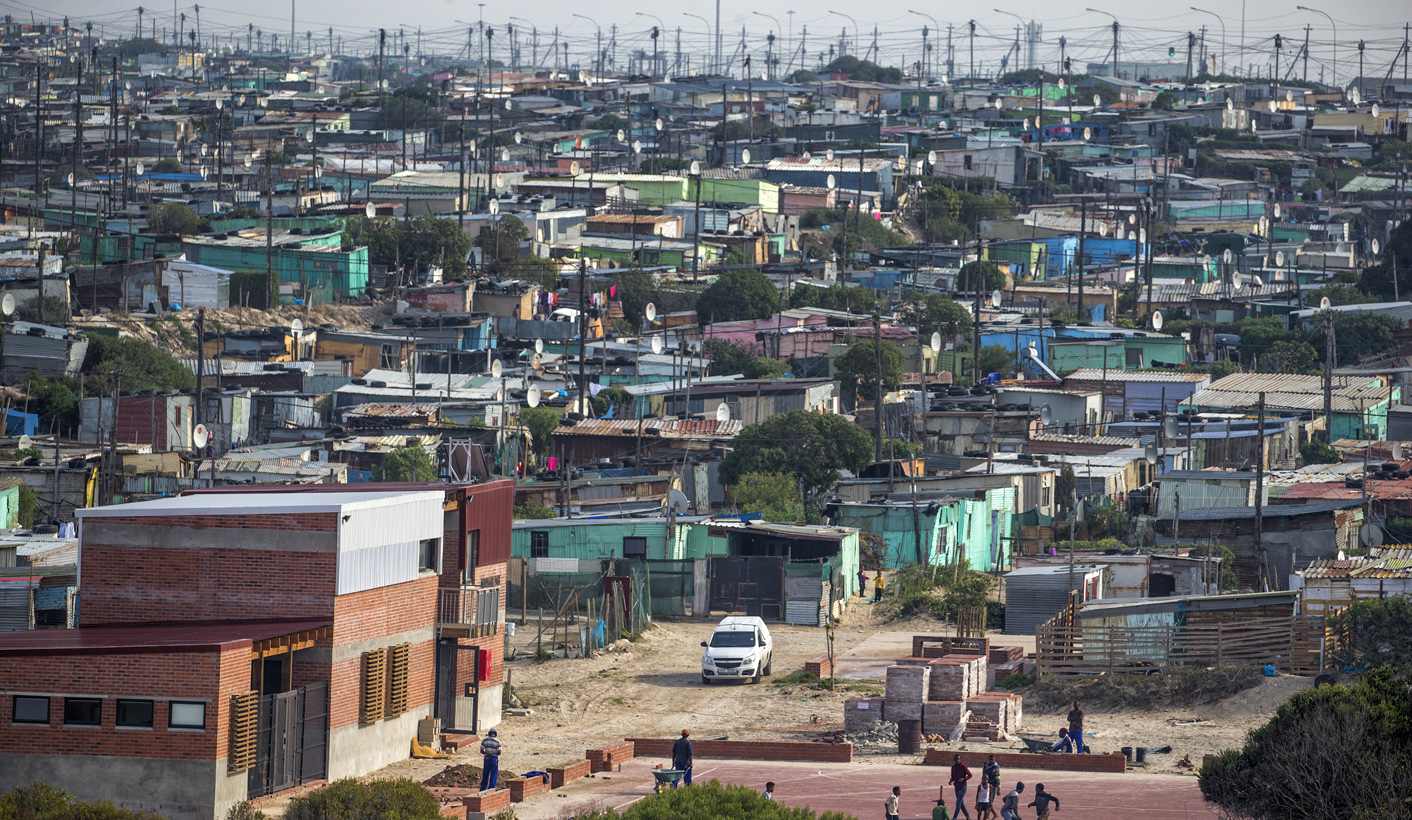
The most vulnerable are pastoralists who live in rural areas and nomadic communities. The Northern Triangle of Central America (El Salvador-Guatemala, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico) has seen droughts and floods increase in recent years. These conditions have led to floods and a decline in rural economies. 75,000 Kenyans may be at risk of riverine flooding if there is not enough action to address emissions.
Many experts predict a rise of suicide, substance abuse and mental health problems due to climate change. The ACA Climate Change Task Force says that people from disadvantaged communities are most at risk of suffering trauma due to climate change.
Climate in Crisis also addresses the impact of environmental colonialism on Indigenous people. In Panama, for example, Indigenous communities had to cope with deforestation, logging, as well as the migration of people from their ancestral homelands.
Costa Rica has seen its urban growth accompanied by a concern for sustainability. Many environmentalists believe that the media has failed to adequately highlight this issue. There are many ways that media can communicate the climate issue better.

Researchers from the Political Psychology Research Group studied several Americans in an effort to understand the significance of the climate crisis. Most of the respondents believed that Earth's current climate was warming. A majority of the respondents believed that this is a serious problem. However, nearly half the respondents were skeptical that human activity is the cause of the warming.
Despite this, the majority of respondents held firm to their original belief that climate changes are real and are a result of human actions. The public's view on climate has not changed, even though the political debate has moved. However, technology is still lacking to address the climate crisis.
The story can sometimes be distorted by soundbites and inability to analyze. The majority of issues are divided roughly 50-50.
FAQ
How can developing countries and communities cope with the effects of climate changes?
Because of their limited access and lack of technology and healthcare, the impact climate change has on developing countries and communities is particularly severe. Temperature, precipitation and sea level changes increase pressure on already finite resources. Already fragile ecosystems are being destroyed by floods or droughts. Rising temperatures can reduce crop yields. This will impact communities with low incomes and food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
The long-term impacts of climate change include resource scarcity, poverty, increased health risks, and an increase of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever. A rising sea level and extreme weather events will increase the risk of flooding, putting lives at stake in coastal areas that often lack the infrastructure or emergency services required to evacuate. To build resilience against these risks, mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions is necessary. Other measures include improved management and better access to water resources.
What role do greenhouse gases play in climate change?
Greenhouse gases play a major role in climate change. They act as an invisible shield around the Earth and trap infrared radiation, warming the atmosphere. Without them, the planet might be much colder that it is now.
Human activity is responsible for the emission of greenhouse gases. This includes burning fossil fuels and other industries. As these activities continue to increase, more heat gets trapped in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the largest greenhouse gas. This is due to fossil fuels like oil, coal, and gas. Methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases (F-gases) are also major contributors to climate change.
Because of human activities, the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased substantially since preindustrial days. This has led worldwide warming and increased temperatures in the oceans as well as all over the planet. It is also causing drastic changes, such as increased storms, droughts, melting glaciers and rising ocean levels.
To avoid more damage from climate changes, humans must reduce their emissions by switching away from fossil energy to increase their use of renewable energy like solar and wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These activities will help lower atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and create a healthier environment for all life on Earth.
What can we do to help the climate change process?
Climate change can be attributed to human activity. In fact, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), humans are responsible for more than 70% of all global warming since the mid-20th century.
The release of carbon dioxide from fossil fuels: When fossil fuels are used, like coal, oil, or gas, they cause the atmospheric formation of carbon dioxide. This increases the already high levels of atmospheric CO2, which acts as a greenhouse gas by trapping heat from Earth's sun and increasing temperatures. This results in higher ocean levels because Arctic ice mellows and causes weather patterns to change around the world, which can lead to severe storms, droughts or floods. These could impact food production and pose a threat to human health.
Deforestation - Trees which store atmospheric carbon dioxide within their trunks, when they absorb it through photosynthesis, are removed by deforestation. Deforestation also raises albedo (the amount of reflected solar radiation that is returned into space) and reduces solar heat absorption by earth's surface, thereby promoting global warming. Also, deforestation can lead to a decrease in local air quality and respiratory problems.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Animal waste releases large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to its composition rich in methane bacteria Eating less or no animal products altogether can be an effective way to reduce your contribution towards global warming from this source alone., Agriculture itself also relies heavily on fertilizers which contain nitrous oxide released into our atmosphere directly harms humans creating smog from ground level ozone harming our respiratory system making polluted air hazardous for life.
In conclusion, while human activity has had an adverse impact on our environment for centuries, technological advances have made it possible to turn our attention towards the future. We can leverage technology through green innovation to help us move forward in our efforts to reduce climate change and keep everyone safe.
What are the impacts of climate change on biodiversity, ecosystems and species?
Climate change can have a variety of impacts on biodiversity, ecosystems, and the environment. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
These climate changes can alter habitat areas and food chains, as well as affect species distributions or population numbers. They could also have significant consequences for biodiversity or the functioning of ecosystems. Hydrological changes can also impact water availability for aquatic species.
Climate change is also causing rising temperatures and more extremes like droughts/floods. This adds to the stress already placed on fragile systems such coral reefs and tropical rainforests. A climate change scenario could see up to 30% loss of animal species by 2050. That would trigger a chain reaction of losses within eco-systems.
Climate change poses a grave threat to biodiversity, but also to human societies that are dependent on functioning ecosystems to provide food, fresh water and timber. To mitigate its effect efforts must be made at all levels to reduce global warming trends and future damages should be avoided where possible with careful management practices.
What are the impacts of climate change on society and the environment?
Climate Change has broad effects on both the environment and society. Climate change will have many impacts on the environment. These changes can have devastating effects on human populations. They may lead to increased instability in communities and intensifying poverty as well as insect-borne diseases.
Already, climate change has had a broad range of devastating effects on society and the environment around the globe. Global temperatures are expected to continue to rise and this will only get worse in the future.
Ocean levels rising due to melting ice caps is one of the most pervasive effects of climate change worldwide. This leads to shoreline erosion at many coasts as well as an increased risk for flooding for coastal communities. Also, saltwater intrusion occurs, which negatively affects freshwater supplies in coastal areas in many countries.
Climate change is causing extreme weather events like heatwaves, droughts and other severe weather to occur in many countries. These events lead to massive destruction of homes, businesses, and even the loss of whole communities. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
The increasing frequency of wildfires that are caused by climate change has also led to devastating consequences for both habitats and those living nearby.
This drastic change in living conditions is often a result of displacement or even refugee situations. When people decide to leave their homes, either involuntarily or voluntarily, it can be because their town has become too dangerous or not habitable due the changed climate conditions.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. Additionally, pest infestations are likely to rise significantly in conjunction with higher temperature extremes (a phenomenon known as the "greenhouse bug") which can cause further damage to agricultural production. This could further affect global food security numbers. As fewer crops become available at poorer nutritional qualities, it may bring additional hardships on marginalized communities already struggling to make ends meets otherwise.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Support Climate Friendly Policies and Companies
There are many ways that individuals can support climate-friendly companies and policies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can also immediately take more practical steps such as switching providers when possible to ones that have a better environmental record or choosing sustainable products over those with higher carbon emissions.
Supporting climate-friendly policies and companies is one of the most important steps in reducing one’s carbon footprint. It can be as simple as changing your daily habits like unplugging appliances and turning off lights when they are not needed. You can also use eco-friendly household products such biodegradable cleaners and composting kitchen scraps to reduce carbon emissions.
Investors who want to support climate friendly policies should search for companies with lower carbon emissions prior to investing. Investors interested in climate-friendly policies should examine their portfolios every so often to make sure they are meeting sustainability standards. Green bond investors might want to make sure that they don't finance activities that cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they remove. Investors should be alert to opportunities where funds can be converted towards green business activities like renewable energy alternatives or other initiatives promoting sustainability, such as community-building projects based on green technologies.