
Nature climate change refers to the alteration of the global climate caused by additional heat from greenhouse gases. This heat is carried from Earth by the atmosphere and oceans. These two interact with each other. Climate changes can be seen in hours or years depending on the exact location. Weather is an important climate determinant, as it can affect the seasonal rainfall conditions. The climate is influenced by the ice sheets, oceans, the carbon cycle and other components. However, many of these elements are slow in response.
The effects of climate change are slow on the deep sea. The delayed response to climate change could be caused by interactions between the deep oceans, ice sheets, and other ecosystems. These processes can have an effect on the frequency of severe events. These feedbacks may account for 20% of mitigation needs by 2050, according to a recent analysis.
Restoring ecosystems is one way to combat climate change. These include natural wetlands and forests as well as coastal ecosystems. These ecosystems reduce the effects of climate change by increasing carbon sequestration. They also protect biodiversity, secure water supplies, and provide cleaner air. They can also encourage synergy between Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Climate change is one the most pressing and difficult science problems of our times. Many scientists are working to understand the causes and implications of climate change. Understanding the impacts climate change has on both nature and society is essential. It can cause dramatic changes in species' adaptive capabilities and overall climate system sensitivity.
The evidence for the cost-effectiveness and effectiveness of climate solutions based on nature is mixed, despite the urgency of this situation. To ensure their reliability, there are several factors. It is not always clear what nature-based solutions will bring. Second, it requires a deep understanding of the biome's ecological resilience and the biome. These solutions can also be difficult to monetize.
A recent analysis however found that nature-based solutions could help to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Natural forests can help reduce flood risk and provide water security. The soil erosion can also be reduced by natural wetlands.

Nature-based solutions offer significant advantages over engineered alternatives. However, their performance is still uncertain. They must be combined quickly with a reduction in greenhouse gas emission. They will also need to be funded and promoted.
Recent research suggests that nature-based climate mitigation solutions are an effective and cost-effective way to mitigate climate change. As long as they're combined with rapid emission cuts, they could contribute to up to 20% of mitigation requirements by 2050.
For instance, natural wetlands can reduce flood risk and help prevent landslides. Natural forests and coastal ecosystems are also good for biodiversity. Some ecosystems are already moving to new states due to climate change. Many species that were once limited to tropical or boreal areas are now moving into temperate habitats.
FAQ
What are the consequences of climate change for society and the environment?
Climate Change has broad effects on both the environment and society. Climate change can have many effects on the environment. These changes could have serious consequences for humans, causing instability in communities, intensifying poverty, insect-borne illnesses, changing human migration patterns, and destroying essential habitats.
Climate change is already having a wide range of sweeping effects on the environment and societies all over the world. This is expected to get worse as global temperatures continue rising.
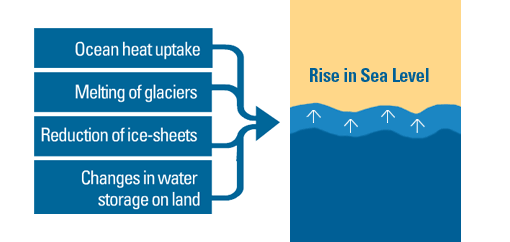
One of the most prevalent effects of climate changes worldwide is the rise of ocean levels as a result of melting ice cap. This leads to shoreline erosion at many coasts as well as an increased risk for flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
Due to climate change, extreme weather phenomena such as heatwaves/droughts frequently occur across many countries in the world. These events result in mass destruction of homes or businesses and can lead to relocation or complete loss of life. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
Additionally, wildfires caused climate change are more common than ever. They can be devastating for both the habitats and the people who live nearby.
These dramatic changes in living conditions can often lead to displacement and even refugee crisis when people leave their homes voluntarily or involuntarily due to their changing climate.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. In addition, pest infestations are expected to increase significantly linked with higher temperature extremes - a phenomenon known as 'greenhouse bug' - leading to further damage to agricultural production that further affects global food insecurity numbers as fewer crops become available at worse nutritional qualities potentially bringing additional hardships upon marginalized populations already barely able make ends meet otherwise.
What is the impact of land use change and deforestation on climate change?
The climate can be directly affected by deforestation and changes in land use. If trees are cut down, or burned, carbon dioxide, one the most important greenhouse gases, is no longer absorbed. Deforestation and burning of trees for agricultural purposes removes less carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
At the same time, changes in land use can also release more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. In addition to methane and nitrous oxide, pesticide and fertilizer use can increase when forests are converted into agricultural lands. Additionally, clearing soils rich in carbon can increase the exposure; soils that are disturbed by farming activities or turned over can release more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
Deforestation, land-use change and other environmental impacts can cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they do. It can also affect regional air quality. As an example, deforestation smoke has been shown to reduce visibility and cause respiratory illnesses such asthma and other conditions. Because of the reduced amount of aerosol particles in our atmosphere, which scatter sunlight off the Earth's surface, these changes can have a cumulative impact on global climate.
In conclusion, both deforestation (and land-use) change have been a major contributor to rising levels of global greenhouse gases emissions. Additionally, they have had negative effects on local airquality that has contributed further to climate changes. If serious efforts to combat climate change are to occur, it should be a top priority to reduce these practices.
What are the roles of individuals and communities when it comes to addressing climate change?
Climate change is a major contemporary challenge. It affects all of us and requires our collective attention as well as individual actions to make a real difference.
Individuals can play an important role in addressing climate change. Everyday behaviors can include anything from reducing waste and consuming consciously, going through changes in lifestyle such as switching to a vegetarian diet, consuming less meat, using public transportation more often, and choosing more sustainable materials in clothing and home decor. They can also be involved in political advocacy, and encourage initiatives within their communities that foster sustainability.
Communities are also key players in addressing climate change on a bigger scale. They can adopt policies that reduce emissions. These include reformulating energy models that are based on renewable sources, encouraging efficient infrastructure for bicycle or electric transport, reducing deforestation and encouraging composting systems for waste disposal. For this mission to succeed, collaboration is key.
Moreover, civic education on the threats posed by climate change, as well as on ways to contribute positively towards tackling it needs to be implemented from the early stages of education acquisition throughout lifelong learning opportunities. This will allow individuals to be more aware and connected to other societies, even if they are not located near us.
Ultimately employers have a major responsibility when it comes to fighting climate change: introducing corporate practices focused on sustainability and opting for green alternatives whenever possible will undoubtedly yield positive results both economically and sociologically speaking.
The collective efforts of individuals, communities and businesses will all play a significant role in addressing global warming and defending humanity from the long-term effects of climate change.
What happens to developing countries when they experience the climate change effects?
Due to limited access, technology, and healthcare systems, developing countries, communities, are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of climate change. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels increase pressure on already scarce resources, with floods and droughts wearing away at already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can reduce crop yields. This will impact communities with low incomes and food insecurity. Moreover, extreme weather events such as heatwaves and hurricanes can result in the destruction of infrastructure and displacement of people, further perpetuating economic inequality.
Climate change will have long-term effects on resources, poverty, and health. This includes an increase in the number of vector-borne disease such as dengue fever or malaria. In addition, there will be a higher risk of flooding due to rising sea levels coupled with extreme weather events putting lives at risk in coastal areas where populations often lack the adequate infrastructure or emergency services needed for evacuation. Building resilience against these risks necessarily involves mitigating greenhouse gas emissions but may require other measures such as improved management of freshwater resources and better access to health facilities which assists with prevention strategies for diseases like malaria.
How can the energy sector be involved in climate change?
It is crucial that the energy sector plays a significant role in climate change. The burning of fossil fuels is a primary source of global warming, caused by releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, trapping heat, and leading to an increase in average temperatures on Earth.
Energy sources must shift away from fossil-emitting energy sources like coal and natural gases and towards renewable energy sources like wind, solar and geothermal to address this problem. This transition can be made through both government policy and incentives, as well as investments in innovative technology like hydrogen fuel cell. Businesses and homeowners can cut their emissions while reducing their electricity bills by investing in infrastructure that supports these renewable sources.
Another option is to move away from polluting transport options such as petroleum-fueled vehicles and towards electric cars or public transport. Governments can help lead society's transition from oil-based infrastructures to cleaner alternatives by funding research into battery technologies and encouraging consumers to make investments in cleaner modes.
To reduce carbon footprints, companies should adopt green business practices. For example, better insulation in offices and production facilities. This can dramatically reduce operational costs, while improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives should be championed at all levels, not just at company level but also at government. Raising taxes on pollution products encourages individuals and businesses to stop using harmful practices. While this may be a financial outlay for polluters, providing vouchers for or subsidy for low-carbon products can create a continuing market to support sustainability efforts. It is important to recognize that tackling climate change takes a lot of effort from both the private and public sectors.
What are the causes and consequences of climate change?
Climate change has become a global problem due to an increase in human-generated greenhouse emissions. These gases are mostly emitted by fossil fuel combustion for electricity and transportation. These emissions lead to a greater amount of sun's energy being trapped in Earth’s atmosphere, which results in rising temperatures.
Climate change can also be caused by population growth, land clearing, destruction of ecosystems and energy consumption, over-grazing, and deforestation. This further decreases the number natural carbon sinks that absorb CO2 in the atmosphere. Climate change can also come from natural forces, such as changes in solar energy.
These combined human activities result in overloading Earth's capacity to properly balance its energy budget, leading to an average increase of 1 degree Celsius globally since pre-industrial times. Glaciers are melting faster than they become and sea levels are rising as the oceans absorb most of the heat energy. Other consequences include water shortages, droughts, and extreme weather events such as floods and hurricanes that are caused by heavy rainfall on saturated soils.
To prevent further damage, we must reduce our carbon footprint and cut our emissions as soon as possible. We can also take action now to mitigate the already severe effects of climate change. Along with reducing our dependence upon fossil fuels to generate electricity, it is important to invest in renewable sources like wind turbines or solar cells that do not emit harmful pollutants into nature. Also, reforestation is a sustainable practice that can restore balance to the delicate planetary cycles which are essential for our survival.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy to Support a Low-Carbon Transition
Clean energy is renewable energy that doesn't emit greenhouse gases or produce polluting emissions. It includes technologies such a solar photovoltaic (Solar Photovoltaic), wind power, hydroelectricity and geothermal energy. Investing in clean energy sources can bring many environmental advantages, including a reduced reliance on fossil resources, less air pollution, better electrical access, and greater reliability to remote locations.
By buying shares in companies involved in developing clean energy technologies, investors can get involved in these projects. This includes investing directly in stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) related to clean energy. Investors may also be interested in direct investments in start ups or venture capital projects that fund research and technology development.
Investors in clean energy support innovation that reduces the harmful effects of traditional sources of electricity generation. This investment may also lead to increased economic development by creating jobs related to the production of renewable energy systems that require skilled labor and engineers. Lastly, investors may see a return on their investment in clean energy through tax incentives programs. These incentives encourage green technology investments such as solar panels, wind farms, and biomass heat production systems.
We can help the transition to low-carbon by investing in companies that create electricity from renewable resources.