
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, also known as the IPCC, is an intergovernmental body that was established in 1988 under the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP). It is a worldwide body that brings scientists, policymakers, researchers and others together to discuss and find solutions to climate change. The IPCC's goal, is to educate the globe about climate change and propose possible solutions.
The Panel is composed of non-partisan representatives who have been appointed by the governments. These government representatives pick qualified scientists to represent their interests at IPCC meetings. Representatives recruit experts to help with the preparation of reports. Governments are also able to nominate their own scientists to serve on the Panel. This does NOT necessarily mean that the government endorses the views expressed by a scientist.

IPCC's structure includes three working groups that focus on different aspects of climate science. One group deals with the physical science, the other two deal with adaptation and mitigation. Each of the working groups is led by a Co-Chair. Both Co-Chairs are members of the IPCC Bureau. They assist the chair with the selection of authors, and in preparing for meetings.
The Working Group I, which is the first, focuses on the physical science and impacts of climate change. It includes the Met Office Hadley Centre which is one of the top climate research centres worldwide.
The Working Group II assesses the effects of climate change on people and ecosystems, and proposes measures to mitigate climate change. The Australian Government is one of its members. It manages the DFAT Trust Fund, and contributes to IPCC decisions.
Working Group III, a third working group examines mitigation strategies and assesses the impact of climate-related changes on both the economic as well social dimensions. Its members include the World Bank and the United States Agency for International Development.
The IPCC creates reports through volunteer groups made up of hundreds scientists from all around the world. They examine scientific literature to make recommendations based primarily on new research. An IPCC assessment report provides a comprehensive overview of current climate knowledge. A report can be published in 4 parts.
Summary for Policymakers refers to a summary of all the IPCC reports. This report is most appealing to journalists as well as the general public. IPCC reports are available to everyone and are reviewed by a variety of experts. The IPCC collaborated with practitioners and communications experts to produce the Fifth Assessment Report.
IPCC hosted an Expert Meeting on Communication in February 2016. IPCC made several recommendations at this meeting on effective communication. Some of these recommendations were incorporated into the IPCC's outreach activities and the IPCC website.
The Special Report on Ocean and Cryosphere Changes in Climate - September 2019 was released by the IPCC. The IPCC is now preparing for the Sixth Assessment Report, (AR6). This report provides an extensive review of current climate-change knowledge. This report, like previous assessments reports, will be published in sections.
FAQ
How are extreme weather events related to climate change?
Extreme weather events, such as heat waves, floods, droughts, cyclones, storms, and hurricanes are directly linked to global warming. Global warming has caused an increase of atmospheric temperatures.
Climate scientists claim that the frequency of extreme weather related disasters has more then doubled since 1980. As sea temperatures rise, so do wind patterns. This has an impact on the normal distribution and strength of hurricanes and storms across different regions of the planet.
The 2015 El Nino event caused warm water to move towards South America, leading to rising temperatures at alarming rates and heavy rains that caused floods in Peru (and Bolivia) causing property damage and displacement. Many places, including Antarctica, have experienced their highest temperatures ever. This indicates a direct relationship between global warming trends as well as the frequency or occurrence of extreme weather events all over the globe.
Another example is Hurricane Irma, which struck in 2017, causing $50 billion in economic damage not only to Florida, but also to other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba, and others. This proves once again that climate change has been responsible for an increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) concluded, "Human activities are increasing the severity current climate change." This naturally leads worldwide to more severe, intense, and frequent natural disasters. There is strong evidence of humans' involvement with extreme weather events occurring frequently around us all.
How can the energy sector be involved in climate change?
The role of the energy sector in climate change is immense. The burning of fossil fuels is a primary source of global warming, caused by releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, trapping heat, and leading to an increase in average temperatures on Earth.
This requires energy sources to move away from carbon emitting sources like natural gas and coal, and instead shift towards renewable energy sources, such solar, wind, or geothermal. This transition can be made through both government policy and incentives, as well as investments in innovative technology like hydrogen fuel cell. Businesses and households can both reduce their carbon footprints while also lowering their electricity bills by investing into infrastructure that supports this use of renewable resources.
Alternatives include moving away from polluting vehicles like petrol-powered cars and moving to electric vehicles or public transportation. The government has great power to help societies transition away from oil-based infrastructures. They can support research into battery technology and encourage consumers to invest in cleaner modes.
In order to reduce their carbon footprint, companies need to adopt green business methods. These include installing better insulation systems in offices and creating energy efficiency plans for manufacturing facilities. This can drastically reduce operational expenses while also improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must be championed not just at the company level but also at the government level for them to be truly effective; increasing taxes on pollution products encourages individuals to switch away from harmful practices without forcing them financially outcompeting polluters by providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products will create an ongoing market to support sustainability efforts moving forward. The private and public sector must work together to combat climate change. Providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products and switching to cleaner energy sources will create a market that supports sustainability efforts.
What are the effects of climate change on the environment and society?
Climate Change has broad effects on both the environment and society. Climate change can have many effects on the environment. These changes could have serious consequences for humans, causing instability in communities, intensifying poverty, insect-borne illnesses, changing human migration patterns, and destroying essential habitats.
Already, climate disruption is already having profound impacts on the environment and society around the world. Global temperatures are expected to continue to rise and this will only get worse in the future.
One of the most widespread effects of climate change is the rising ocean levels due to melting of ice caps. This causes shoreline erosion along many coastlines and increases the risk of flooding for coastal communities. Also, saltwater intrusion occurs, which negatively affects freshwater supplies in coastal areas in many countries.
As a result, extreme weather events such heatwaves or droughts are common in many countries. These events cause massive destruction to homes, businesses, and sometimes even wipe out entire towns. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
The increasing frequency of wildfires that are caused by climate change has also led to devastating consequences for both habitats and those living nearby.
These drastic changes often lead to displacement or refugee crises. People move out of their homes involuntarily or voluntarily when their communities become unsafe or uninhabitable due to the altered climate.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. Pest infestations will increase due to higher temperatures - a phenomenon called the 'greenhouse bug'. This can further impact global food insecurity as fewer crops are available with poorer nutritional qualities, potentially creating additional hardships for marginalized populations that otherwise would be barely able to make ends meet.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change can have many impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems. Climate change is affecting ecosystems and wildlife today.
Changes to climate conditions can have drastic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning ecosystems. Changes in the hydrological cycle can also affect water availability for aquatic species.
Climate change is also causing rising temperatures and more extremes like droughts/floods. This adds to the stress already placed on fragile systems such coral reefs and tropical rainforests. The climate change will lead to the extermination or decline of as many as 30% of animal species in 2050. This could cause further destruction of ecological communities.
Climate change poses a significant threat to biodiversity and human societies, as well as to ecosystems that provide food, water, timber, or other services. At all levels, efforts should be made to decrease global warming trends. Future damage should be avoided if possible through careful management.
How does climate change impact marine life and oceans around the globe?
What are the effects of climate change on oceans and marine life around the globe?
Since its inception, climate change has had a significant impact on the oceans and marine life of the world. The constant oceanic heating caused by the loss of the ozone layers causes severe disruptions to marine ecosystems, leading to coral bleaching and species declines.
Climate change also causes unpredictable weather conditions and stronger storms. These extreme surges can be deadly for coastal areas. Furthermore, changes in temperature may reduce oxygen levels in water systems resulting in "dead zones" where abundant marine life becomes sparse.
Climate change is also contributing to ocean acidification, caused by excess carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere that accumulates within the oceans. Ocean acidification can raise pH levels, making it difficult for animals to adapt like crabs, clams or oysters.
Higher temperatures can alter the natural habitats of certain species by changing their locations or shrinking them, making them uninhabitable. This increase in ocean stress accelerates already high extinction rates amongst many species worldwide causing a severe imbalance between predators and prey that might eventually lead to complete extinctions.
The ripple effect of climate change affects entire ecosystems. It can directly or indirectly impact multiple species through evaporation, lower water volumes, and sharp temperature shifts. Climate change is transforming the future of all life forms on our planet, not just those living on land but those living below the ocean surface.
How does human activity contribute to climate change?
Climate change can be attributed to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (IPCC), human activity is responsible for more that 70% of all global warming.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This adds to already existing levels of atmospheric CO2, which act as a "greenhouse gas" by trapping heat from the sun in Earth's atmosphere and increasing temperatures even further. This leads to higher ocean levels as Arctic ice melts and scrambles weather patterns around the world leading to deadly storms, droughts, and floods which could affect food production and endanger human health.
Deforestation - Trees which store atmospheric carbon dioxide within their trunks, when they absorb it through photosynthesis, are removed by deforestation. Deforestation also raises albedo (the amount of reflected solar radiation that is returned into space) and reduces solar heat absorption by earth's surface, thereby promoting global warming. Also, deforestation can lead to a decrease in local air quality and respiratory problems.
Farming: Between 14% and 18% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions are attributed to animal agriculture each year. Animal waste releases large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to its composition rich in methane bacteria Eating less or no animal products altogether can be an effective way to reduce your contribution towards global warming from this source alone., Agriculture itself also relies heavily on fertilizers which contain nitrous oxide released into our atmosphere directly harms humans creating smog from ground level ozone harming our respiratory system making polluted air hazardous for life.
In conclusion, while human activity has had an adverse impact on our environment for centuries, technological advances have made it possible to turn our attention towards the future. We can leverage technology through green innovation to help us move forward in our efforts to reduce climate change and keep everyone safe.
Climate change: What is it and how can it happen?
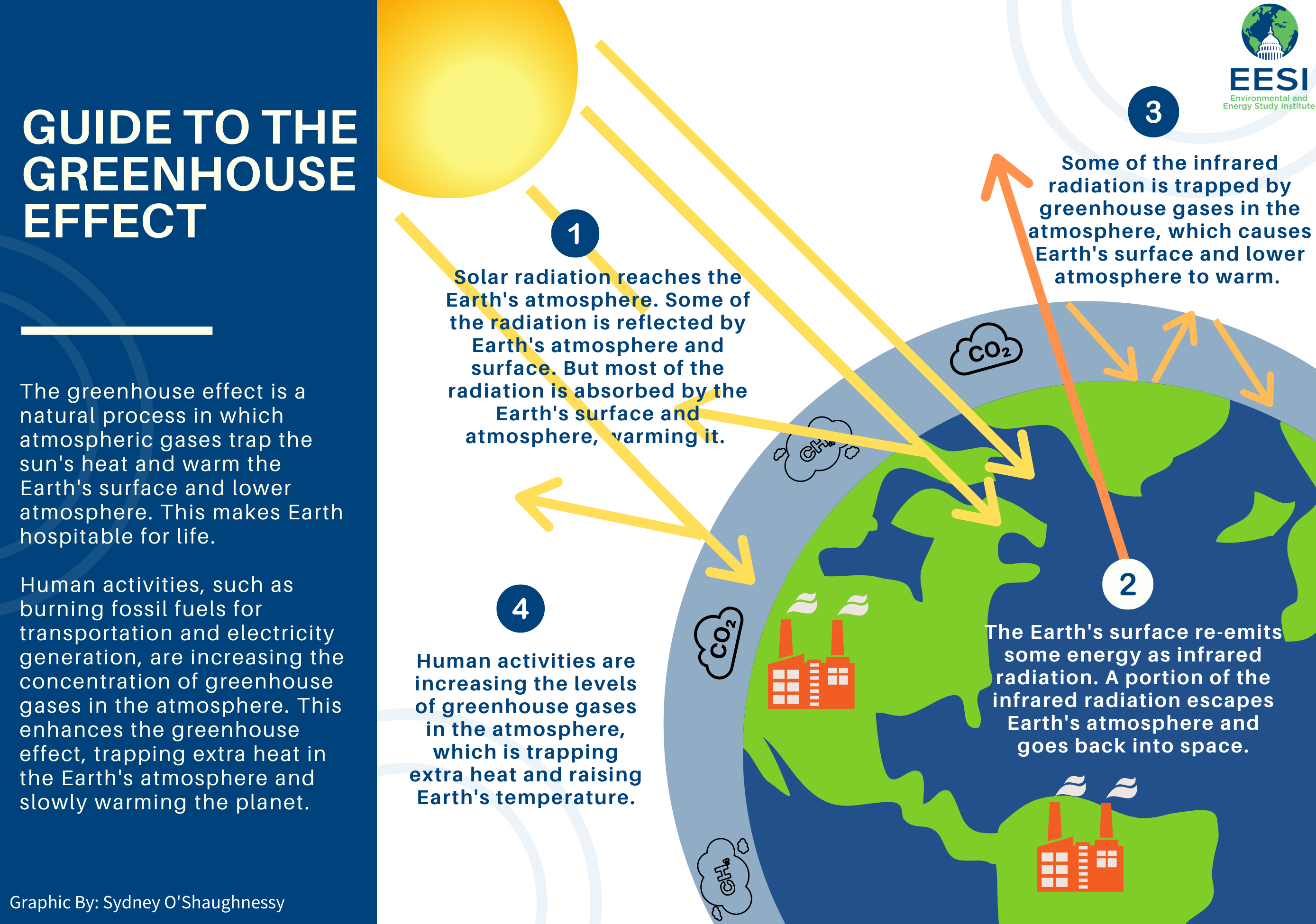
Climate change refers to the long-term shifts in global weather patterns that are caused by an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat and cause global temperatures to rise, which can lead to a variety of changes in weather patterns and climate. These include rising sea levels and melting glaciers, severe storms and droughts as well as widespread coral reef bleaching and species extinction.
Climate change is primarily caused by human activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels for electricity, transportation, and cutting down forests. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
Global greenhouse gas emissions are also influenced by deforestation, which contributes about 15-20%. Deforestation is when trees are cut down and burned. This releases carbon dioxide from the trees back into the atmosphere. Additionally, forests act as a natural carbon sink that removes CO2 from the air; without this absorptive capacity, carbon dioxide levels will continue to rise with devastating consequences for ecosystems around the world.
Not only does CO2 release into the atmosphere but it also releases other harmful gasses, such as methane(CH4) and nitrogen oxide (N2O). Methane has been used extensively in industrial processes and contributes significantly to atmospheric warming while N2O is emitted primarily from agricultural soil management activities like fertilization or tilling which release excess levels of nitrogen into soil leading to N2O production upon microbial contact.
To minimize climate change humanity must make concerted efforts across social, economic, and political institutions to reduce these emissions drastically and transition away from our dependence on fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind power, or low-carbon hydrogen fuels. A smart approach to reducing atmospheric contamination and preventing CO2 accumulation could be to replace polluting fossil-fuel technologies with ones that encourage zero-waste living. It is possible to reduce our environmental footprint by taking responsibility. Conservation measures such as reforestation can help protect biodiversity and absorb large amounts of CO2 into the environment. This will be a powerful tool in helping to solve the climate crisis and restore balance for future generations.
Statistics
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Support Climate Friendly Policies and Companies
Individuals can take several actions to support climate friendly policies and companies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can also immediately take more practical steps such as switching providers when possible to ones that have a better environmental record or choosing sustainable products over those with higher carbon emissions.
It is important to reduce one's carbon footprint in order to support climate-friendly companies and policies. It is possible to make simple changes such as turning off lights and unplugging devices, moving by public transport or carpooling, using eco-friendly household goods like biodegradable cleaning products and composting kitchen wastes instead of adding them to the landfills.
Investors who want to support climate friendly policies should search for companies with lower carbon emissions prior to investing. Investors who are interested in supporting climate friendly policies should research companies that emit less carbon than they own. They should also review their portfolios frequently to make sure they comply with the sustainability standards set by them. Green bond investors will want to ensure their investments do not fund any activity that releases more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere than it takes away. Investors should consider any opportunities that could allow funds to be used for green business activities. These include renewable energy alternatives as a way to promote sustainability and community-building projects using green technologies.