
The climate system has both positive and negative feedbacks. These feedbacks act as counteracting mechanisms to climate forcing and are an integral part of the climate system. The magnitude of changes in radiative fluxes is a common indicator of the impact of a feedback. These measurements are called feedback parameters. These measures are useful in estimating the magnitude of climate-related changes that could occur due to a particular perturbation.
For example, the carbon-climate feedback parameter (g) is a measure of the relative impact of a warming surface on land carbon inventories. This measure is important because it measures the extent to which warmer climates alter the land's carbon content. However, it is not a comprehensive measure for the climate feedback.
Similar to the carbon–concentration feedback parameter (b), it measures the degree to which an increasing atmospheric CO2 content increases the ocean's CO2 uptake. Like the carbon-climate feedback parameter, b is a function both of land and ocean CO2. However, the magnitude of b decreases when CO2 concentrations are higher.
Sea ice and cloud feedbacks are other examples of feedbacks. Both of these processes have a significant impact on the polar areas. These interactions are more important in the poles than in other regions. These interactions can be simulated by climate models. These processes can also been estimated by using observations.
The largest water vapour feedbacks occur in the tropics where an increase of water vapor strengthens the initial heat source. Water vapour is a greenhouse gas that increases the planet's temperature. Furthermore, an increase water vapor leads to a greater warming of the ocean. Some of these feedbacks are relevant to geological events.
The ice formation-ocean warmth storage feedback measure the effect of climate changes on the storage of thermal energies. This is a natural measurement since an increase or loss of heat results in an increase or storage of heat. This effect can be quantified in several ways and is useful for understanding climate change mechanisms.

Carbon-cycle feedbacks are another important component of the climate system. These feedbacks are related to changes in ocean and land carbon inventories. These parameters can be diagnosed by comparing the differences in simulations that are constrained by observations. In order to be useful, the parameters should only be compared with respect to the same forcing scenario. However, the differences in model outputs may be substantial and the uncertainties large.
The best estimates of total feedback are in the range of two to five K. These estimates are not perfect, but they are close. Using these estimates, the best-known equilibrium temperature change is about 2.9 K. With an additional 3.5 W m-2 of CO2, the expected equilibrium temperature changes range from 2 to 5.8 K. Therefore, the standard radiative feedback framework is a good approximation. Nevertheless, these parameters need to be adjusted to account for non-radiative feedbacks such as land and ocean evaporation and condensation.
FAQ
What is the current status of the global climate, and how is it changing in the future?
The current global climate state is one of unprecedented change and uncertainty. Unprecedented levels in atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing global temperatures to rise significantly. This can lead to droughts and heat waves as well changing rainfall patterns, melting Polar ice caps, ocean acidification and rising sea levels.
These changes already have a profound impact upon ecosystems around the globe and are causing extinctions as well as disruption of habitats. These changes are also threatening billions of lives and livelihoods, especially those living in areas of resource scarcity or poverty.
Because of the increase in average surface temperatures from human activity, the number of extreme weather phenomena such as hurricanes and cyclones has been increasing steadily over time. As temperatures rise, this trend will likely continue.
Climate change has global consequences. It can affect everything, from food insecurity and displacement to communities that are forced to relocate due to severe weather events or rising sea levels. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
While some countries have made progress in reducing carbon emissions, or implementing renewable energy initiatives, global action has not been taken at the level necessary to combat these changes. In order for us to prevent further disruption and devastation from climate change all nations must come together and take urgent action now while at the same time planning for adaptation in an increasingly uncertain world.
Climate change: What is it and how can it happen?
Climate change refers to the long-term shifts in global weather patterns that are caused by an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which causes global temperatures rise. This leads to many changes in weather and climate. This could lead to rising sea levels, melting glaciers and extreme storms and dry spells, widespread coral reef bleaching, and the extinction of species.
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. These include burning fossil fuels, transporting electricity, cutting down trees, and farming livestock. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
Another major contributor to the global greenhouse gas emission is deforestation. It accounts for around 15-20%. The atmosphere is effected by the carbon dioxide stored in trees when they are cut down or burned. Furthermore, forests act like a natural carbon sink and remove CO2 from air. Without this absorption capacity carbon dioxide levels will continue rising with devastating consequences to ecosystems all over the world.
Not only does CO2 release into the atmosphere but it also releases other harmful gasses, such as methane(CH4) and nitrogen oxide (N2O). Methane has been used extensively in industrial processes and contributes significantly to atmospheric warming while N2O is emitted primarily from agricultural soil management activities like fertilization or tilling which release excess levels of nitrogen into soil leading to N2O production upon microbial contact.
The collective efforts of social, economic and political institutions must be made to drastically reduce the emissions and shift away from fossil fuel dependence. Replacing technologies that use polluting fossil fuels with smart solutions that promote zero-waste living could be an effective approach to decreasing atmospheric contamination while simultaneously reducing heating due to CO2 accumulation. It is possible to reduce our environmental footprint by taking responsibility. Conservation measures such as reforestation can help protect biodiversity and absorb large amounts of CO2 into the environment. This will be a powerful tool in helping to solve the climate crisis and restore balance for future generations.
What are the ways climate change can be mitigated or reduced?
There are various measures that can be taken to reduce and mitigate the effects of climate change. There are many ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These include using more sustainable energy and alternative sources of power. Protecting forests and wilderness habitats. Investing in sustainable transport systems. Strengthening early warning systems for natural disasters. Creating a research program about the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Investing in green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Developing sustainable consumption habits and implementing appropriate environmental regulations in all areas of society. Additionally increasing public education about climate change is also important as it encourages people to feel responsible for their actions.
How are extreme weather events related to climate change?
Extreme weather events, such as heat waves, floods, droughts, cyclones, storms, and hurricanes are directly linked to global warming. Global warming has led to increased atmospheric temperatures.
According to climate scientists in 1980, extreme weather-related natural disasters have increased by more than twice the rate. Rising ocean water temperature causes sea levels to go up as well as changing wind patterns. This has an impact on the normal distribution and strength of hurricanes and storms across different regions of the planet.
2015 El Nino brought warm water towards South America. This led to increasing temperatures at an alarming pace and heavy rains that caused floods and displacement in Peru, Bolivia and other countries. Many places, including Antarctica has recorded its highest temperature ever. This is an indication of a strong correlation between global warming trends & the occurrence/frequency of extreme weather phenomena around the globe.
Another example is Hurricane Irma in 2017. It caused $50 billion economic loss to Florida and other states, as well as Puerto Rico and Cuba. This is yet another proof that climate change is responsible.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change concluded that humans are increasing the severity and frequency of climate change. This naturally leads to more severe, frequent, and intense natural catastrophes worldwide. It also provides strong evidence about human involvement in extreme weather events that occur at regular intervals around us all.
How does human activity contribute to climate change?
Climate change can be attributed to human activity. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) states that humans are responsible more than 70% for global warming in the past 20 years.
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This adds to already existing levels of atmospheric CO2, which act as a "greenhouse gas" by trapping heat from the sun in Earth's atmosphere and increasing temperatures even further. This leads to higher ocean levels as Arctic ice melts and scrambles weather patterns around the world leading to deadly storms, droughts, and floods which could affect food production and endanger human health.
Deforestation. Trees that absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in photosynthesis will be effected by being cut down. Reduced forest cover can also increase albedo, which is the amount of reflected sunlight coming back into space. This reduces solar heat absorption at the surface of the earth and promotes global warming. The deforestation of forests can also affect the local air quality, which is directly linked to respiratory problems.
Farming: The animal agriculture industry contributes 14%-18% of total anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases globally every year. Due to the high levels of methane bacteria in animal waste, methane gas is released into the atmosphere in large quantities. Changing your diet to less or no animal products can help reduce this contribution. Smog from ground-level ozone can harm our respiratory system and make our lives more hazardous.
Conclusion: Human activity has had a profound impact on the environment for centuries. However, technology has made it possible to leverage green innovation and make eco-friendly efforts to combat climate change. This will ensure that everyone is safe while prospering in nature.
What is the role of greenhouse gases in climate change?
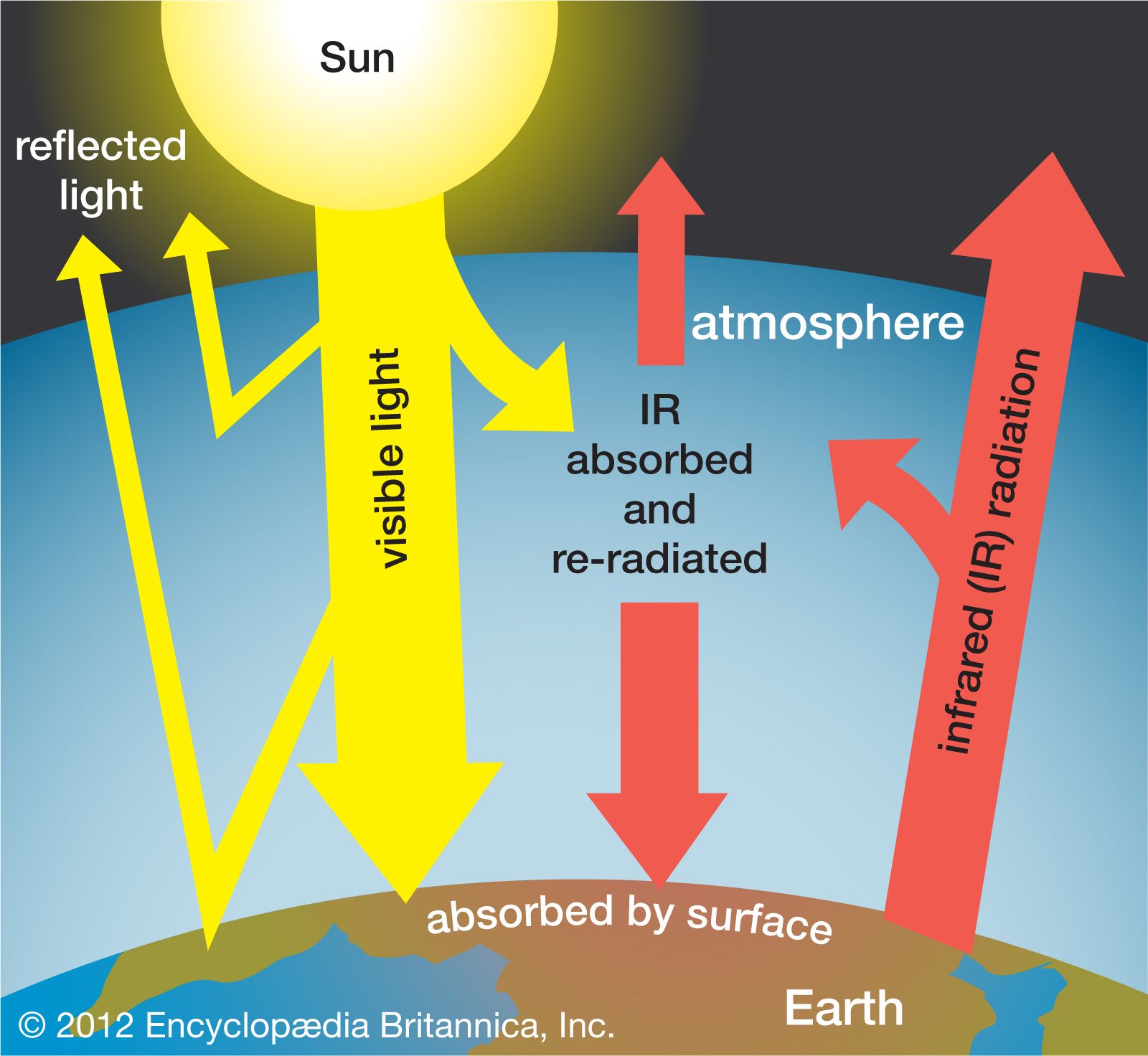
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket around the Earth, trapping infrared radiation and warming the atmosphere. Without them, the planet might be much colder that it is now.
Human activity is responsible for the emission of greenhouse gases. This includes burning fossil fuels and other industries. These activities increase the heat that is trapped in the atmosphere. This leads to higher temperatures and more extreme weather events.
The most prevalent greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide, which is released from fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal. Methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases (F-gases) are also major contributors to climate change.
Due to human activities, the concentration of greenhouse gasses has increased dramatically since preindustrial time. Global warming has resulted in an increase of temperatures around the world and in our oceans. It is also causing changes such as more intense storms and droughts, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels.
To prevent further climate change-related damage, humanity must reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by moving away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources like wind or solar power. You can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reforestation and adopting farming methods that allow soil to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
What role can individuals and communities play in combating climate change?
Climate change is one our greatest contemporary challenges. This is a problem that affects everyone. We must all pay attention to it and take action individually to make a difference.
Individuals can play an important role in addressing climate change. It is possible to make small changes in your everyday life such as reducing waste or consuming more conscious, switching to vegetarianism, eating less meat, taking public transportation more often, and using more sustainable fabrics for clothing and home decor. They can also get involved in political advocacy to promote sustainability-related initiatives in their community.
Community involvement is key in addressing climate changes on a larger scale. They can also implement policies to reduce emissions, such as promoting electric and bicycle transportation, encouraging the use of efficient infrastructure, reducing deforestation, and encouraging waste management systems. This mission requires collaboration between communities in different cities and countries.
Moreover, civic education on the threats posed by climate change, as well as on ways to contribute positively towards tackling it needs to be implemented from the early stages of education acquisition throughout lifelong learning opportunities. This will help individuals become aware of the issues at stake and understand our interconnectedness with other societies further away from our geographical location but similarly affected by global warming
Employers have a significant responsibility in combating climate change. Introducing corporate practices that are focused on sustainability and choosing green alternatives whenever feasible will undoubtedly result in positive economic and sociological outcomes.
Individual actions, community policies and business transformation can all be a part of creating solutions to global warming. Together they will help humanity avoid the longer term negative effects of climate change.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy and Support a Transition to a Low Carbon Future
Clean energy is a type of renewable power that doesn't produce any pollution or emit carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. It can include technologies such as solar photovoltaics, wind power and hydroelectricity. Investing in clean energy sources can bring many environmental advantages, including a reduced reliance on fossil resources, less air pollution, better electrical access, and greater reliability to remote locations.
By buying shares in companies involved in developing clean energy technologies, investors can get involved in these projects. This could be done by investing in publically traded stock, mutual funds, or ETFs related to renewable energies. Direct investments in start-ups and venture capital projects can be an option for investors to help fund research and development of clean energy technologies.
Investors who invest in clean energy are supporting innovation that helps reduce harmful emissions from traditional sources of electricity generation. This investment can also help increase economic development through the creation of jobs in the production and engineering of renewable energy systems. Lastly, investors may see a return on their investment in clean energy through tax incentives programs. These incentives encourage green technology investments such as solar panels, wind farms, and biomass heat production systems.
By investing in companies that produce electricity from renewable sources such as sun, wind and water, while avoiding any activities that might harm the environment, you can help support the transition towards a low-carbon future, while also reaping economic benefits.